Uterine Fibroids Overview
WHAT ARE
FIBROIDS?
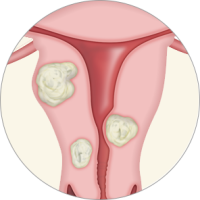
Fibroids, also known as uterine fibroids, leiomyomas, or myomas, are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that grow within the muscle tissue of the uterus.
WHO IS AT RISK?
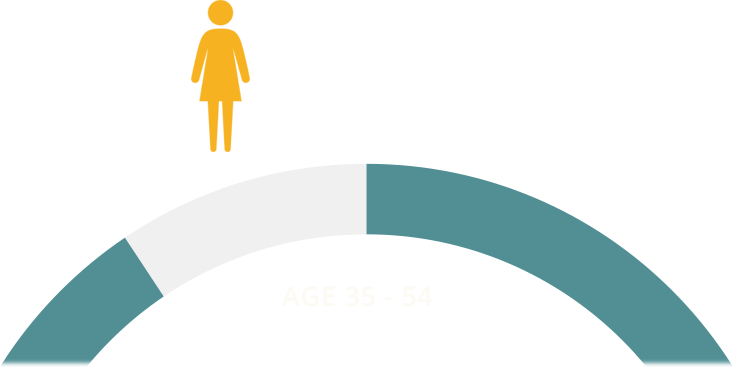
Since uterine fibroids are the most common tumors within the female reproductive system, all women are at a potential risk of developing them.
The majority of uterine fibroids are diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 54. However, fibroids can occur in women younger than 35.
What are fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are an extremely common diagnosis for women. In fact, out of every four women in America, three of them usually have fibroids during their lifetime. Only one in three women usually experiences symptoms, so it can easily go undiagnosed.
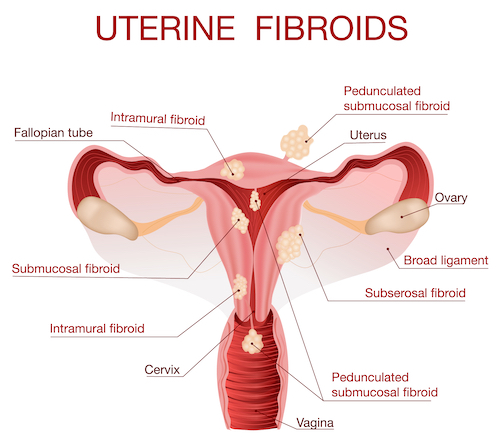
Fibroids, also known as uterine fibroids, leiomyomas, or myomas, are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that grow within the muscle tissue of the uterus. There are four types of fibroids. They are called Intramural fibroids, Subserosal Fibroids, Submucosal Fibroids and Pedunculated Fibroids. It is common for a woman to have multiple fibroid tumors and it may be difficult to understand which fibroid is causing specific symptoms.
The most common fibroid symptoms include:
- Pain
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Abdominal pressure
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Frequent and incomplete urination
- Constipation
- Painful sex
Causes:
The living tissue of the fibroid needs oxygen and nutrients to grow and repair itself, just like other cells in your body. When the fibroids grow too large or too quickly, the blood vessels supplying the fibroids are no longer able to provide enough nutrients to meet the needs of the fibroid. When this happens, the cells of the fibroid begin to die, causing extreme pain and abdominal discomfort. This process is called degeneration. Untreated, fibroid degeneration can lead to:
- Extreme pain
- Sudden rupture of the fibroid
- Infertility
- Bleeding
- Cancer
- Damage to the uterus
WHO IS AT RISK?
WHAT DOES THE RESEARCH SAY?
- Studies demonstrate the prevalence of fibroids in 20-40% of women older than 35 years of age.1
- African American women are three times more likely to develop uterine fibroids with an earlier age of onset.2
REFERENCES:
Wallach, E. E. (1992). Myomectomy. In Thompson, J. D., & Rock, J. A. (Eds.), Te Linde’s Operative Gynecology, 7th (pp. 647-662). Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott.
Huyck, K. L., Panhuysen, C. I., Cuenco, K. T., et al. (2008). The impact of race as a risk factor for symptom severity and age at diagnosis of uterine leiomyomata among affected sisters. Am J Obstet Gynecol, Feb;198(2):168.e1-9.
